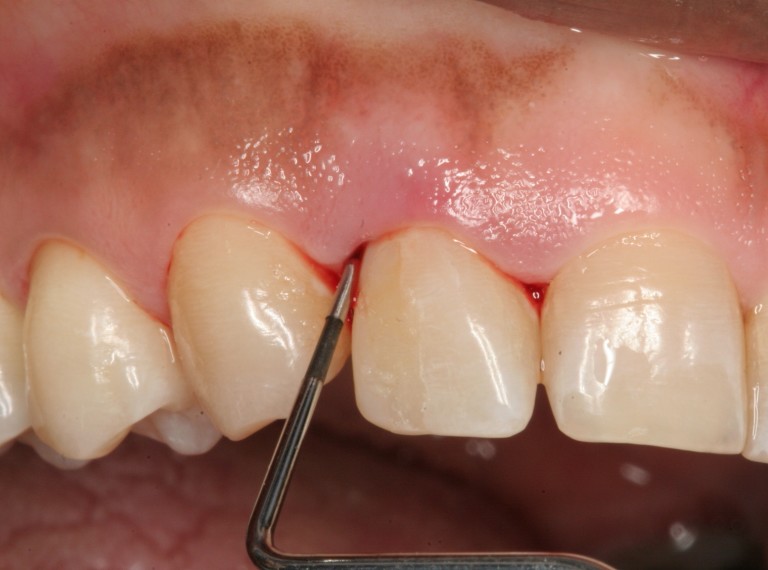
What do you know about periodontal disease?
In fact, periodontal disease is extremely common but the signs are often overlooked, when it’s so serious then patients are treated. Then the consequences may be loss of teeth or inflamed deep into the bone.
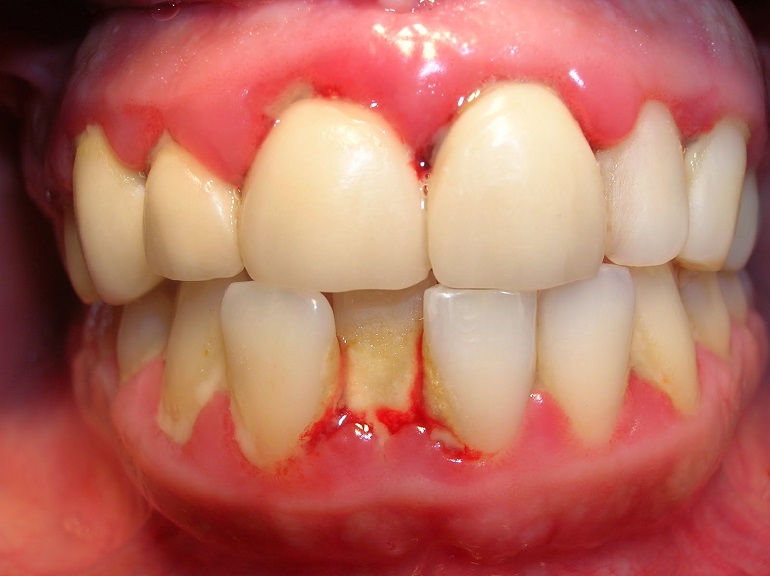
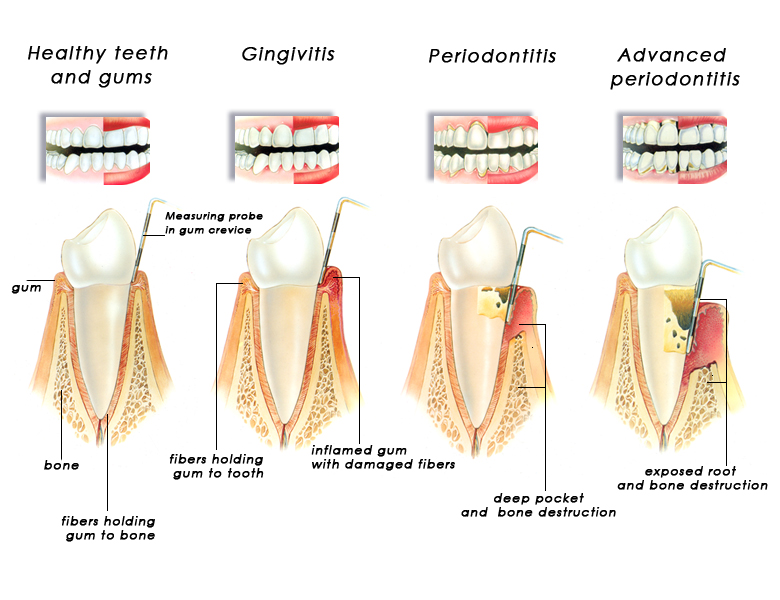
Simply understood, periodontal disease is the stage of progression of gum disease.
1. Gingivitis stage:
The patches of food that attach to the neck of teeth, it make up the adhesive membrane that build up day after day, and they are the environment where bacteria exist and produce toxins that cause gum inflammation. Gingivitis is characterized by signs of redness, swelling, and sometimes bleeding during brushing. At the onset of gum recession and bleeding, the gum and tooth alignment becomes loose, resulting in the root can be partially exposed.
At this stage, gingivitis is just beginning, can be restored by proper oral hygiene, will help you retain strong teeth while keeping bone (bone cover the tooth root) and the connective tissue (between teeth and bones) is not damaged.
2. Periodontitis:
Bacteria begin to penetrate between the teeth and gums. The oral environment is favorable for anaerobic bacteria growing underneath the receding gum area. From there, it creates an inflamed gingival cavity just below the normal gingival margin.The surrounding connective tissue and alveolar bone show signs of inflammation. Toxins released by bacteria along with enzymes secreted by the body to fight inflammation begin to destroy bone and connective tissue around the teeth.
During this period, the bones and fibers that support the teeth (which help hold the teeth) are destroyed and can’t be restored. Good oral hygiene and hygienic measures now only work to prevent further progression of the disease.
Some factors contribute to the more severe periodontal disease:
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Braces are not good
- Filling of concave teeth
- Oral hygiene are not good
- Grinding teeth
- Pregnant or using oral contraceptives
- Have immune system problems such as diabetes or AIDS …
3. Periodontitis progresses:
Once the periodontitis has progressed, the inflammatory gingival cavity invades deeper and more bone tissue as well as the gum tissue is destroyed. Finally, the entire supporting structure will be lost.Tooth gradually are not tight and if periodontal inflammation is not properly treated, it can lead to permanent tooth loss (tooth will lose or dentist must be removed).
Some signs that the disease is beginning to progress:
- Gums bleeding when flowing teeth
- Tartar at collar teeth, swollen red gums, bleeding easily
- Smelly breath, when pressed into the gums with pus.
- Teeth are not tight
Treatment of periodontitis:
If the disease is found in the early stages of gingivitis, the doctor can treat it with a dental cleansing procedure.
If the disease has progressed through the period of periodontitis, progressive gingivitis, the treatment will be deeper such as “root canal curettage” or “bottom cleaning”, this intensive cleansing removes the plaque with the bacteria below the gum line, help the healing gums. This procedure can be performed several times depending on the severity of the disease.
In severe periods, when the sacs are deep in between the teeth and gums, the doctor performs the surgery to thoroughly clean the infected area. In this situation, if gums are missing, your doctor will perform grafts for you.
How to prevent periodontal disease?
- Avoid smoking
- Brush at least twice a day, preferably after meals and before bed.
- Brush the correct method according to the doctor’s instructions, using a soft bristle brush, brush along the crown and teeth to help remove excess food plaque.
- Use dental floss to thoroughly remove remaining plaque. Avoid sticks that cause bleeding easily lead to gingivitis.
- Periodic dental check-ups help detect any signs of illness and prompt treatment.
Quoc Binh Dental Clinic